Model#
If you are already familiar with the concepts, take a look at the BGE models!
Embedder#
Embedder, or embedding model, bi-encoder, is a model designed to convert data, usually text, codes, or images, into sparse or dense numerical vectors (embeddings) in a high dimensional vector space. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning or key features of the input, which enable efficient comparison and analysis.
A very famous demonstration is the example from word2vec. It shows how word embeddings capture semantic relationships through vector arithmetic:

Nowadays, embedders are capable of mapping sentences and even passages into vector space. They are widely used in real world tasks such as retrieval, clustering, etc. In the era of LLMs, embedding models play a pivot role in RAG, enables LLMs to access and integrate relevant context from vast external datasets.
Reranker#
Reranker, or Cross-Encoder, is a model that refines the ranking of candidate pairs (e.g., query-document pairs) by jointly encoding and scoring them.
Typically, we use embedder as a Bi-Encoder. It first computes the embeddings of two input sentences, then compute their similarity using metrics such as cosine similarity or Euclidean distance. Whereas a reranker takes two sentences at the same time and directly computer a score representing their similarity.
The following figure shows their difference:
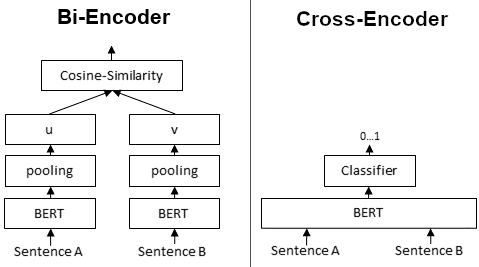
Bi-Encoder & Cross-Encoder (from Sentence Transformers)#
Although Cross-Encoder usually has better performances than Bi-Encoder, it is extremly time consuming to use Cross-Encoder if we have a great amount of data. Thus a widely accepted approach is to use a Bi-Encoder for initial retrieval (e.g., selecting the top 100 candidates from 100,000 sentences) and then refine the ranking of the selected candidates using a Cross-Encoder for more accurate results.
